Scientists are working to develop a synthetic blood that may be obtainable for medics to make use of in an emergency when common blood is just not obtainable.
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
disguise caption
toggle caption
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
Tens of 1000’s of individuals bleed to dying every year in america earlier than they’ll get to a hospital. That is as a result of ambulances, medical helicopters and army medics cannot routinely carry blood, which might go unhealthy too quick with out ample refrigeration.
So scientists have been on a quest to develop synthetic blood that might be saved in powdered type and reconstituted by medics on the spot to avoid wasting lives.
On the College of Maryland College of Medication in Baltimore, the place a few of this analysis is being carried out, a white rabbit lies on the ground of a cage. It is in a “particular intensive care unit that we have created for our rabbit resuscitation,” says Dr. Allan Physician, a scientist on the college.
Physician’s workforce simply drained blood from the animal to simulate what occurs to an individual who’s hemorrhaging from an harm, similar to from a automotive crash or battlefield wound.
“This rabbit continues to be in shock. You may see he is mendacity very nonetheless. It is as if he was on the scene of an accident,” says Physician. “If we did not do something, it will die.”

Dr. Allan Physician is main the synthetic blood analysis on the Heart for Blood Oxygen Transport and Hemostasis on the College of Maryland College of Medication in Baltimore. He additionally co-founded an organization, KaloCyte, to develop the blood substitute.
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
disguise caption
toggle caption
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
However Physician and his workforce are going to avoid wasting this rabbit immediately. They’ll fill his veins with one thing they hope will lastly allow them to realize a objective that has stymied researchers for many years: growing secure and efficient synthetic blood.
“Good bunny,” says Danielle Waters, a technician on Physician’s workforce, as she gently lifts the rabbit and begins infusing him with three massive syringes of synthetic blood.
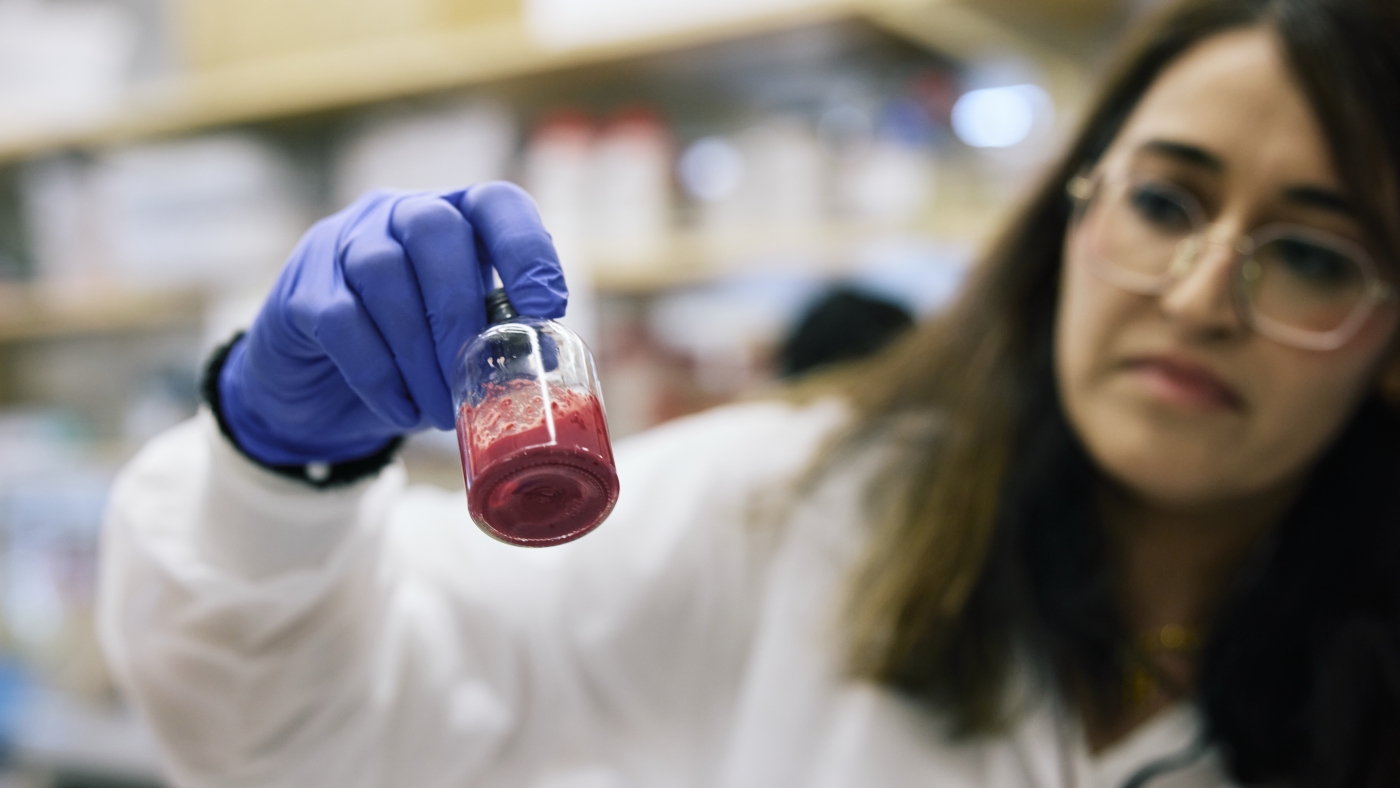
Physician’s workforce makes artificial blood from hemoglobin, the protein that nourishes the physique with oxygen. The researchers extract hemoglobin from expired blood and enclose the protein in a bubble of fats, primarily creating synthetic crimson blood cells.
The protecting bubble is the innovation that Physician thinks will resolve the protection issues attributable to different makes an attempt at making artificial blood. These different efforts additionally used hemoglobin, however uncovered hemoglobin might be poisonous to organs, he says.
“We now have to veil the hemoglobin inside a cell. It is a synthetic cell that makes it secure and efficient,” Physician says.
The scientists then freeze-dry the synthetic crimson blood cells right into a powder that may keep good till an emergency.
“It is designed in order that in the mean time it is wanted, a medic can combine it with water and inside a minute you will have blood,” Physician says.
“It’s shelf-stable for years, and it may be simply transported. And so the purpose is so that you may give a transfusion on the scene of an accident,” Physician says.
Stopping preventable deaths

Freeze-dried synthetic blood developed in Physician’s lab might be reconstituted with water and infused into an animal check topic. In the end the analysis workforce hopes to check this in folks, utilizing product derived from human crimson blood cells.
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
disguise caption
toggle caption
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
Along with use in emergency medication, army medics may additionally use synthetic blood to avoid wasting wounded troopers. The Protection Division is spending greater than $58 million to assist fund a consortium that is growing Physician’s artificial blood, together with different elements that allow clotting and keep blood strain.
“The No. 1 reason for preventable dying on the battlefield is hemorrhage nonetheless immediately,” says Col. Jeremy Pamplin, the undertaking supervisor on the Protection Superior Analysis Tasks Company. “That is an actual downside for the army and for the civilian world.”
Physician is optimistic his workforce could also be on the point of fixing that downside along with his synthetic crimson blood cells, dubbed ErythroMer. Physician co-founded KaloCyte to develop the blood and serves on the board and because the agency’s chief scientific officer.
“We have been capable of efficiently recapitulate all of the features of blood which can be vital for a resuscitation in a system that may be saved for years at ambient temperature and be used on the scene of an accident,” he says.
Promising ends in animal checks

Scientist Ruby McAslan works on hemoglobin purification within the chilly room at KaloCyte on the Heart for Blood Oxygen Transport and Hemostasis on the College of Maryland College of Medication.
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
disguise caption
toggle caption
Eli Meir Kaplan for NPR
Again within the lab, Waters is completed infusing all three vials of artificial blood into the rabbit after about 10 minutes.
“My goodness, bunny, you probably did it,” she says as she locations him again in his cage. “There we go.”
Nearly instantly, a monitor monitoring the rabbit’s very important indicators present his coronary heart price, blood strain and different vital metrics have recovered from close to dying to almost regular. He is beginning to resume regular conduct, similar to transferring round on his personal and ingesting water.
“The actually good signal is that he is very pink,” Physician says. “His eyes are pink. His ears are pink. That is a very good signal he has plenty of oxygen in his blood and it is being successfully distributed. He is respiration comfortably and calm. It is superb how rapidly it may possibly work.”
Physician’s workforce has examined their synthetic blood on tons of of rabbits and up to now it appears to be like secure and efficient.
“It could change the way in which that we may handle people who find themselves bleeding exterior of hospitals,” Physician says. “It might be transformative.”
Like different rabbits utilized in these experiments, this animal will later be euthanized so the researchers can carry out a necropsy to ensure the synthetic blood did not trigger any tissue or organ harm.
Human trials nonetheless to return
Whereas the outcomes up to now appear to be trigger for optimism, Physician says he nonetheless must show to the Meals and Drug Administration that his synthetic blood can be secure and efficient for folks.
However he hopes to start out testing it in people inside two years. A Japanese workforce is already testing an analogous artificial blood in folks.
“I am very hopeful,” Physician says.
Different specialists stay cautious. Many promising makes an attempt to create synthetic blood finally proved unsafe.
“I believe it is a affordable strategy,” says Tim Estep, a scientist at Chart Biotech Consulting who consults with corporations growing synthetic blood.
“However as a result of this discipline has been so difficult, the proof will probably be within the medical trials,” he provides. “Whereas I am total optimistic, putting a wager on anybody expertise proper now could be total tough.”